This is the 2nd article in a new ‘futures’ series authored by Remo Prinsloo, a Lead Solution and Futures Architect for Accela in the Asia Pacific region.
“Metaverse”, there is a good chance you heard of this or are actively participating in this realm. Since Facebook changed their parent company’s name to “Meta” in 2021, this term experienced an increase in popularity. However, the concept of a Metaverse has existed since the 1940’s. So, what is the Metaverse and how will it affect the future of and our communities?
Metaverse defined
A very simplistic description of the Metaverse could be a digital destination providing an alternative community, fully interactive and integrated to allow the users various experiences from the possible to the impossible while engaging a user’s senses. It transcends physical borders, demolishes biased and discriminatory boundaries, and allows previously impossible avenues of engagement.
The concept, introduced by Klaus Schwab in 2015 as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), explains the benefits of a Metaverse and how we will use technology and digital capabilities to transform the way we live. With the Metaverse, we can alternate between the physical world and the digital world. In essence, for the first time since the invention of the computer, the digital realm is materializing as a physical tangible ecosystem that is just as influential and existential as the real world we live in.
This interchangeability between these two realms is where the challenge lies. The connection between physical identity and digital identity becomes important. Regulation, legislation and oversight of the digital realm are important things that will need to be considered as the innovation and expansion of services increase exponentially.
Talking ‘bout revolution
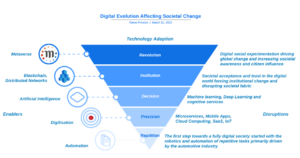 Our digital journey as a society accelerated from the moment we started to automate tasks using digital means. Since then, we have gradually evolved on what is possible with tech and achieved milestones along our digital journey.
Our digital journey as a society accelerated from the moment we started to automate tasks using digital means. Since then, we have gradually evolved on what is possible with tech and achieved milestones along our digital journey.
Each of the enablers provides the next step in the digital adoption process enabling the necessary reassurance and reliance to increase digital capabilities. Blockchain is the current enabler, marking a turning point for financial and governmental institutions to transform and completely re-imagine their operations.
The Metaverse will again take this journey one step further providing a platform for change. Whether this will be positive or negative is yet to be seen. Social experimentation will see the dawn of new ideas, shaping the way we think about things and banishing physical restrictions, laws of nature and possibly challenge the moral status-quo. As the community adoption of the Metaverse increases so will the influence it yields, not just over governments but the whole world.
Digital community
A “fully digitized government agency” is not about the latest technology, but how an agency uses the available technology to its advantage. The common misconception when considering the digitization of operations, is the reduction of staff. This is rarely the case. The successful outcome of digitization results in seamless integration and augmentation of business processes. The transition of repetitive and monotonous tasks allows employees more opportunity to improve and innovate in the work environment.
Over the last couple of years, we have moved from thinking about “online-business” as just “business.” Every interaction in our lives these days involves some digital element. The digital agency will utilize these advancements in payments, integration, security and other digital technologies to engage and collaborate with their customers, adopting a similar “on-demand” service model. Powered by digital capabilities like artificial intelligence, chat bots, mobile applications and digital community chatrooms, digital agencies will be rewarded with higher citizen engagement, satisfaction and ultimately trust.
Opportunities exist for agencies to address and remediate the loss of inclusion that this platform will bring. Inclusion requires participation, If you don’t join you are automatically excluded and hence could alienate and disadvantage those that choose not to participate. This could further divide communities and increase unintended bias and discrimination having a severe impact that includes financial exclusion, reduced employment opportunities and social exile. Combatting this growing concern with digitization requires empathy and sympathy, elements only human presence can provide. Balancing digital mediums with human oversight is a fundamental principle ensuring that the digital agency can provide services across its diverse customer groups.
Inclusivity and community engagement
Humans naturally ignore the things we find uninteresting, unengaging or irrelevant. We do however want to be kept abreast of any news that impacts or interests us. We would like to know what the weather is like today before stepping out of the house, or which roads we need to avoid when driving to work. Having these updates forms a crucial part of our comfort and ultimate trust. The digital agency will engage with their citizens in this manner in order to serve, inform and help with moderation and in a non-intrusive manner.
Decentralized and distributed
One of the most effective ways to ensure continuity is the distribution and decentralization of services. The internet provides an unrestricted, accessible protocol for the sharing of data, the Metaverse provides an unrestricted, accessible habitat. The power of this concept should not be underestimated. Where the internet provides the freedom to know, the Metaverse will provide the freedom to be, and could become a valuable tool for governments and agencies wanting to have a clearer understanding of the needs and wants of their citizens without bias, judgment and prejudice but more importantly without interference and censorship.
Active and passive participation
The fully digital agency will require an active participation in the Metaverse in order to accommodate community engagement. Registration of digital identities and more importantly the validation of these identities becomes key to the success of this new frontier. The balance between active and passive participation is also important. Passive participation requires the agency to be a mere observer, restrained from engaging divisive and controversial topics. A government agency should always remain neutral and promote bipartisan collaboration between its community members. Seoul has already invested resources to explore this area and develop a metaverse platform for their government, finding new ways to promote tourism and provide education and civic services.
Digital identities and avatars
The Metaverse will create the opportunity for everyone to assume an identity, or multiple identities if he or she so chooses. The management and monitoring of these identities will become a crucial part of government agencies to correctly associate a person with his online presence.
Anonymization will have its place in this new realm, but when business is conducted, votes are given and money is exchanged, the identity should be verified, confirmed and vetted for fraudulent and criminal association. Avatars will also play a major role in this environment, whether you are a funpunk or a bored ape, your representation will be associated with your identity and carry the same weight as your driver’s license, a fingerprint or retinal scan.
Govtech adoption
Govtech platforms will need to incorporate web3 and metaverse concepts as part of their integration design and enterprise architecture. User access, identity management, user experience (UX), decentralized integration and usage of off-chain oracle services will need to be considered. The govtech platform in itself may be doing away with traditional front-end portals and mobile applications, utilizing these new concepts and platforms to provide services to their citizens. Accela provides access to most of the Civic Platform via restful API’s. Accela also provides a developer SDK that can be used by third party vendors to design and build mobile applications and integrations independently.
Conclusion
For the first time in history, technology offers citizens the power to decide how they are governed. Will we choose micro-governance – where governing areas are divided and locally managed through citizen participation and preference increasing diversity – or will we choose macro-governance and the rise of the singularity? Both of these options are viable given our current technological capabilities and both could very easily be adopted from a virtual ecosystem that in the end could dictate our physical freedoms and restraints.
The manipulation of the human mind can very easily be achieved through digital means as we already saw the last few years. We should expect that future technology breakthroughs will increase our ability to share information more quickly and efficiently, and this will further compress time and space within an expanding network of connected individuals.
The growth of these concepts is outpacing our authorities’ capabilities to protect its citizens from malicious entities on these platforms. The only way to achieve this is for government agencies to actively participate and embrace these new technologies with caution.



